Seismic inversion is a powerful technique used in geophysics to help us better understand the Earth’s interior. It is a type of seismic imaging method which uses data from seismic waves to create a 3D image of the subsurface of the Earth. By applying this technique, we can gain valuable insight into the structure and composition of the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core. In this blog post, we’ll explore how seismic inversion works, what it can tell us about the Earth’s interior, and the potential applications of this technology.
What is Seismic Inversion?
Seismic inversion is a process of extracting physical properties from seismic data. Seismic inversion is used to gain a better understanding of subsurface structures in the Earth’s interior. This process involves converting seismic waveform data into a useful information about the subsurface environment. Seismic inversion can be used for a variety of tasks, such as estimating rock properties, imaging geological features, and characterizing hydrocarbon reservoirs.
Seismic inversion works by taking the seismic data from an area and running it through a set of equations that convert the data into physical parameters that can be used to infer the structure and composition of the subsurface. Seismic waves are generated when an energy source, like an earthquake, produces a shockwave that propagates through the Earth’s crust. The shockwave is recorded by sensors called seismometers, which measure the energy of the wave at different points in time and space. Seismic inversion uses this data to calculate values such as velocity, density, and reflectivity at each point in time and space. These values are then used to build a 3D image of the subsurface structures.
Seismic inversion is an invaluable tool for geologists, allowing them to gain a better understanding of what lies beneath the surface of our planet. By using seismic inversion, scientists can learn more about how the Earth’s structure and composition have evolved over time. This knowledge can then be used to make informed decisions about resource extraction and other activities related to the Earth’s interior.
Why is Seismic Inversion Important?
Seismic inversion is a technique used to analyse seismic data, which helps us to understand the physical properties of the Earth’s subsurface. By studying seismic waves, researchers can get an insight into the Earth’s interior, such as the shape of rock layers, the size of faults and fractures, and the type of rocks that make up the Earth’s subsurface. With this knowledge, scientists can better understand the geological processes taking place beneath our feet, enabling them to develop better strategies for managing natural resources and mitigating risks associated with earthquakes and other geological hazards.
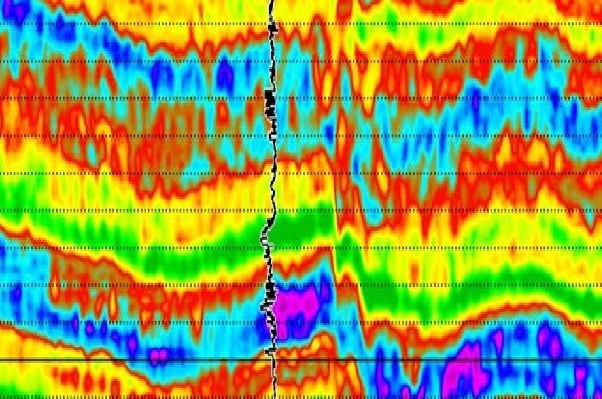
The use of seismic inversion has also become increasingly important for the oil and gas industry. By studying seismic data and analysing the Earth’s structure, companies can get an idea of where hydrocarbon reservoirs may be located, improving their chances of success when drilling for oil and gas.
In short, seismic inversion is a powerful tool for understanding the Earth’s subsurface. Through this technique, we can gain a deeper understanding of how the Earth’s interior works and better plan for natural disasters or for developing natural resources.
How Does Seismic Inversion Help Us Understand The Earth’s Interior?
Seismic inversion is a technique used by geologists and seismologists to gain a better understanding of the interior structure of the Earth. By using seismic waves to measure the physical properties of subsurface layers, seismic inversion can give us an insight into the physical characteristics and composition of the Earth’s mantle, core, and crust.
Seismic inversion helps us to determine the acoustic velocity of rocks. This is important because it can tell us about the density, temperature, and composition of rocks, as well as give us an indication of any tectonic activity that may be taking place below the surface. It can also be used to identify geological features such as faults and fractures, which can provide valuable information about the geological history of an area.
By combining seismic data with other data sources, such as gravity and magnetics, we can create detailed models of the Earth’s interior. These models can be used to map out subsurface structures, determine their properties and assess their potential impact on seismic hazards or resources. They can also help us understand how plate tectonics works, as well as how global climate change may be affecting our planet’s structure.
In short, seismic inversion is an invaluable tool for geologists and seismologists to help them gain a better understanding of the Earth’s interior. With its help, we can learn more about what lies beneath our feet and how it may be changing over time.
